doi: 10.58763/rc202341
Scientific and technological research
Control of heritage assets and their relationship to physical sanitation and accounting information in the municipalities of Lima
Control de bienes patrimoniales y su relación en el saneamiento físico e información contable en las municipalidades de Lima
Remilda Castañeda Ramos1
![]() *,
Dina Arias Diaz1
*,
Dina Arias Diaz1
![]() *, Abrahan Braulio Santos
Maldonado1
*, Abrahan Braulio Santos
Maldonado1
![]() *
*
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this study was to determine the relationship between the control of patrimonial assets and physical sanitation and accounting information in the municipalities of Lima. It was based on a quantitative, cross-sectional, descriptive, correlative and non-experimental methodology. In terms of the sample, the study group for the present investigation comprised all the personnel working in the administrative and accounting areas of the municipalities of Lima and basing the inquiry into a non-probabilistic sampling for convenience, resulting in a total of 40 collaborators. Statistical software SPSS and Pearson were used for data analysis to contrast hypotheses. Under Pearson's statistical correlation test, a robust correspondence was evidenced between the variable control of patrimonial assets and physical sanitation and the accounting information of the municipalities of Lima under study with a Pearson=0.933. In addition, a bilateral significance of 0.000 was evidenced, promulgating a significant relationship between the control of patrimonial assets and physical sanitation and accounting information in the municipalities of Lima.
Keywords: Management audit, accounting, control, finance, public sector.
JEL classification: H11; M41; H83.
RESUMEN
El propósito de este estudio se centró en determinar la relación que existe entre el control de bienes patrimoniales y el saneamiento físico y la información contable en las municipalidades de Lima. Se fundamentó en una metodología cuantitativa, de corte transversal, descriptivo, correlativo y no experimental, en cuanto a la muestra, el grupo de estudio para la presente investigación estuvo conformado por todo el personal que se encontraba laborando en las áreas administrativas y contables de las municipalidades de Lima y fundamentándose la investigación en un muestreo no probabilístico por conveniencia, resultando en un total de 40 colaboradores. Para el análisis de los datos se hizo uso del software estadístico SPSS y Pearson para contraste de hipótesis. Se evidenció bajo la prueba estadística de correlación de Pearson una correspondencia muy fuerte entre la variable control de bienes patrimoniales y saneamiento físico y la información contable de las municipalidades de Lima objeto de estudio con un Pearson=0.933; aunado a ello, se evidenció una significancia bilateral de 0.000, lo que promulgó que existe una relación significativa entre el control de bienes patrimoniales y el saneamiento físico y la información contable en las municipalidades de Lima.
Palabras claves: Auditoria de gestión, contabilidad, control, finanzas, sector público.
Clasificación JEL: H11; M41; H83.
Received: 25-08-2022 Revised: 12-10-2022 Accepted: 15-12-2022 Published: 13-01-2023
Editor: Carlos Alberto Gómez Cano, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0425-7201
1Universidad Peruana Unión. Lima, Perú.
Cite as: Castañeda, R., Arias, D. y Santos, A. (2023). Control de bienes patrimoniales y su relación en el saneamiento físico e información contable en las municipalidades de Lima. Región Científica, 2(1), 202341. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc202341
INTRODUCTION
The Peruvian public sector has been characterized by issuing numerous legal provisions in recent years. It is mostly related to implementing actions to improve accounting information so that public entities' control of assets and liabilities accurately reflects their entire patrimonial, financial, and operational situation (Infante & Moquilaza, 2021; Mite, 2018).
In turn, the existence of audit reports on the control of patrimonial assets from years ago, carried out on 40 public sector organizations, pointing out that there were always opinions that contained qualified opinions, negative opinions, or disclaimers of opinion (López et al., 2018); based fundamentally on what is related to the physical, legal and accounting reorganization of patrimonial assets and, of fixed capital. Likewise, other elements such as inventories, receivables, payables, and other asset and liability accounts have constantly influenced the control of own accounts, physical reorganization, and accounting data over the years (Mendoza et al., 2018; Paima, 2018).
In this regard, Articles 3 and 4 of Law No. 29608, approved by the Congress of the Republic, provide for reordering public sector accounting, which will help government agencies access supporting documents for their financial records. To this end, the Auditor General of the Republic has advised the Congress of the Republic, the Budget Commission, and the General Account of the Republic to evaluate and propose legislative initiatives to establish accountability for reporting, to evaluate the rules for physical and legal reorganization and the conduct of fixed asset inventories in order to amend legislation (Melo et al., 2022; Andara & Peña, 2022).
However, the variety of accounting reorganization provisions cannot be implemented in a single administrative act, so most public entities have found it necessary to start their reorganization actions with one of the large asset accounts, such as account 1503 (cars, machinery, etc.) (Guevara et al., 2018). On the other hand, accounting professionals in the official sector often refer to the International Public Sector Accounting Standards (IAS SP) because these are necessary for preparing financial statements (Sanchez, 2022).
Thus, during the years of exercise, all public entities were obliged to assume the responsibility of complying with the standards, directives, and guidelines that had been issued on the procedures to be followed for the physical and accounting reorganization of assets (Quiroz, 2022). However, due to various factors, interpretation and practice have been limited; most public agencies have opted for hiring duly trained professionals, individuals, or legal entities capable of enforcing compliance with the standards, directives, and guidelines (financial statements). Hence, the municipalities of Lima are no strangers to this circumstance.
From the above and taking into account the entity with which the research will be carried out, the following conditions can be expressed:
1) Identifying the accounts in crisis that needed to be reorganized proved to be an easy task, given that there were qualified valuations, negatives, and abstentions in those opinions. In the case of the Control of Movable Property and Physical Maintenance and Accounting Data of the Provincial Municipality of Yanaoca, this is related to account 1503 (Vehicles, Machinery, and Others).
2) Due to the lack of coordination and training of the internal personnel involved in the management of the assets of the Municipality of Lima, there is no department of asset control, nor does it exist in the functional organizational structure of the company, the creation of such a department is necessary to give continuity to the administrative steps that lead to the physical and accounting sanitation through the control of the assets.
3) The lack of internal guidelines establishing the policies to be followed regarding the management of movable assets will lead to negative account balances in account 1503 (Means of transportation, machinery, and related items) if the assets are improperly managed, which will be reflected in the company's balance sheet at the end of the fiscal year.
The above circumstances indicate that, when it comes to interpreting and applying the rules established in the administrative and legal regulations, these are not manifested in the most expeditious and timely manner since there is no chronological order for the acts to be performed, thus not achieving the intention of the regulations regarding the physical reorganization and accounting information of account 1503 (Vehicles, machinery, and others).
When this problem materializes, the administrative, financial, and accounting policy of the company is at risk, leading to an obstacle in the human, technical, and financial resources used to carry out the control over the generic assets and the reorganization, which impedes the fluidity of the reorganization activities. As a result, the required chronological order may not be established, or the organization of the actions to be taken may need to be carried out correctly with the appropriate administrative documents.
Those above would significantly alter the normal development of the entity's operations, so in order to achieve success, it is essential, in addition to good accounting, to have its administrative infrastructure for the reorganization that allows a timely evaluation of the management in terms of the methods of acquisition, use, and depreciation of the company's movable assets. Consequently, the reorganization of the physical space and the accounting data of the County Council are significantly influenced by the management of the patrimonial assets, so a manual of administrative and accounting procedures must be implemented that contemplates the fair and accounting measures to be used by all the regulations used for the physical reorganization and the accounting information of the patrimonial assets of the organization.
Therefore, the main objective of this research is to determine the relationship between the control of patrimonial assets and the physical reorganization and accounting information in the municipalities of Lima. The importance of this research lies in the need to understand how the assets of the municipalities are managed and how this impacts their financial and accounting management.
Proper control of an organization's assets is crucial to ensure the efficient management of resources, avoiding financial losses, and guaranteeing compliance with rules and regulations. In addition, physical sanitation is a necessary task for properly maintaining and conserving heritage assets, which translates into better use of resources and an extension of the useful life of such assets.
In the specific case of the municipalities of Lima, it is vital to understand how the control of their assets is managed since these institutions are responsible for providing public services to the population and for the efficient management of the resources assigned to them. In this sense, this research seeks to determine how the control of patrimonial assets, physical sanitation, and accounting information are related in the municipalities of Lima in order to identify possible problems in the management of resources and propose solutions to improve efficiency and transparency in their management.
METHODS
The study's premise is based on a quantitative method, meaning that the answers to the study objectives were derived from numerical data (Corona, 2016). From the design point of view, the study was cross-sectional since it focused on analyzing the situation of accounting restructuring and capital controls in the 2021 period. Likewise, the research responded to a descriptive, correlational, non-experimental approach (Gómez, 2020). This is because it sought to reconcile the relationship between the dimensions of the independent variable (Control of patrimonial assets - CBP) and the dependent variable of study (Physical Sanitation (SF) and Accounting Information (IF), which promoted evidencing the thread between them; consequently, it is not experimental, since the research variables were not directly manipulated.
The study was of an applied nature, also called constructive or utilitarian, and was characterized by answering the questions formulated about FI, PBC, and SF within the municipalities of Lima. The study group for this research consisted of all personnel working in the administrative and accounting areas of the municipalities of Lima, who were distributed as follows according to the type of work they were assigned to the entities using a non-probabilistic convenience sampling.
|
Table 1. Number of workers in the municipalities of Lima |
||
|
Decree |
Description |
Number of employees |
|
276 |
Administrative careers and public sector rewards |
20 |
|
- |
Localization of services |
10 |
|
1057 |
Special regime of administrative contracting of services |
10 |
|
|
Total |
40 |
Considering that the population under study is limited, a sample of 40 people was considered to include all administrative personnel related to asset control, accounting information, and physical sanitation in the municipalities of Metropolitan Lima. Concerning data collection techniques, a survey was conducted as the main method of obtaining first-hand data to examine the relationship between PBC and changes in the order of movable property records in the metropolitan municipality under study. The offices of five Lima municipalities were visited, where a previously prepared questionnaire was applied to obtain information as accurately as possible. In addition, tools and instruments such as bibliographic and demographic files were used.
The information obtained through the survey and the questionnaire was used for data analysis. To process the data, automated computer tools were required, such as the SPSS 26.0 statistical package, which allowed adequate treatment of the data collected. Likewise, to test the independence of the criteria, inferential statistics were also carried out to see whether the variables analyzed are independent of each other or, on the contrary, have some degree of relationship between them. In this sense, a p-value test was applied against the significance level of the statistical test, accepting the hypothesis that if the p-value is lower than the significance of the test, it was assumed that there is no relationship between physical sanitation, accounting information, and asset control.
In terms of presentation, the Office package was used to provide a clearer view of the study information through its graphic-textual functions; for example, graphs were prepared to accompany the distribution tables of the research variables. In addition, Pearson's statistical parameterization was used for hypothesis testing.
RESULTS
The following section shows all the data collected for the variables, PBC and SF and the FI collected by means of the instrument applied.
Descriptive analysis of the study variables and their dimensions
The percentages according to the collaborators in the study sample established within the five municipalities chosen in Metropolitan Lima are shown in figure 1. In terms of the variable control of patrimonial assets, there was a predominance in the efficient frequency of 57.5% of the study sample; on the other hand, 37.5% had a regular level of perception concerning the variable, and 5% mentioned a deficient level of control of patrimonial assets.
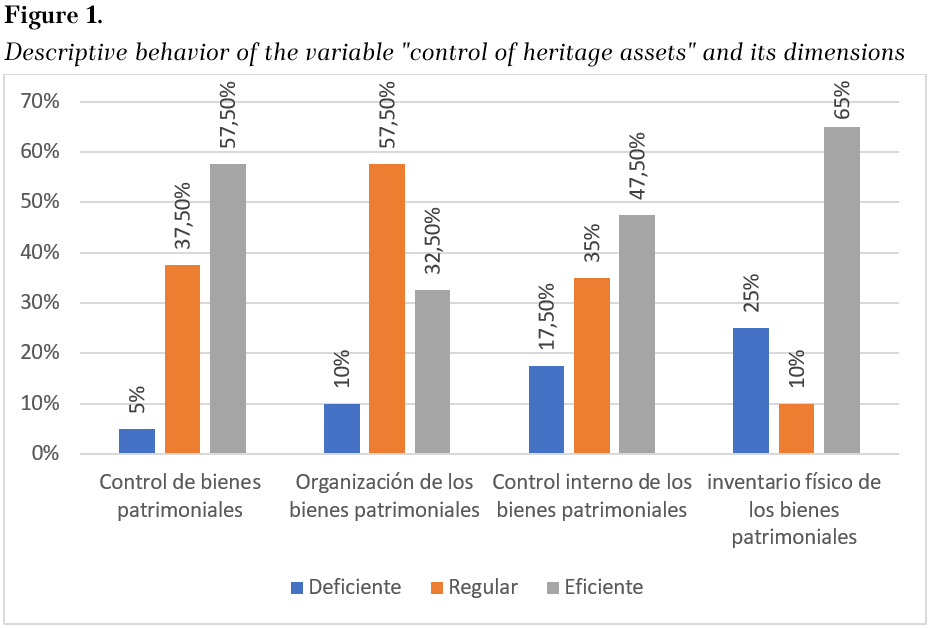
Source: Own elaboration.
Note: the figure appears in its original language
Likewise, concerning the dimension of organization of patrimonial assets, there was a predominant level of regular response with 57.5%, 32.5% mentioned an efficient perception, and 10% mentioned a deficient level of response. Concerning the dimension of internal control of patrimonial assets, the following descriptive levels were extracted: 47.5% have an efficient level, 35% regular, and 17.5% deficient; finally, concerning the dimension of physical inventory of patrimonial assets, the following descriptive parameters were reconciled; 65% efficient level, 25% deficient level, and 10% regular level.
Figure 2 shows the descriptive estimates of the respondents on the behavior of the variable FS and FI. In this sense, concerning FS and FI, a regular descriptive behavior of 47.5% is evidenced regarding managing the variable in question, 40% favorable behavior, and 12.5% unfavorable behavior. The following parameters were established for the dimension of reconciliation of patrimonial assets: 45% favorable, 32.5% unfavorable, and 22.5% regular; for the dimension of accounting records: 42.5% favorable, 37.5% regular, and 20% unfavorable; for the dimension of presentation of FIs: 70% favorable, 25% unfavorable and 5% regular.
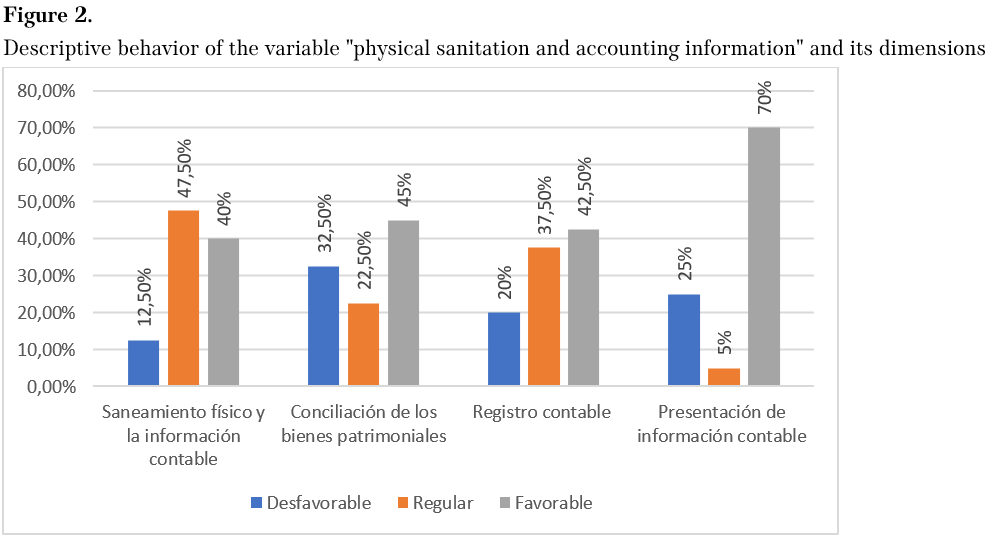
Source: Own elaboration.
Note: the figure appears in its original language
Normality test
On the other hand, the result of the Shapiro-Wilk normality test revealed that for the variable, PBC was (0.316). SF and CI were (0.321) for the variable, with a significance level of 0.120 and 0.061, respectively. This suggests that the research data possess moral behavior if the p-value is greater than 0.05. Therefore, the parametric statistic or Pearson's normality test was used for the study hypothesis testing.
|
Table 2. Normality test for research variables and dimensions |
|||
|
|
Shapiro-wilka |
||
|
Statistician |
Gl |
Sig. |
|
|
Control of patrimonial assets |
,316 |
40 |
,120 |
|
Organization of assets |
,765 |
40 |
,087 |
|
Internal control of assets |
,345 |
40 |
,099 |
|
Physical inventory of assets |
,987 |
40 |
,079 |
|
Physical sanitation and accounting training |
,321 |
40 |
,061 |
|
Reconciliation of assets |
,212 |
40 |
,605 |
|
Accounting records |
,143 |
40 |
,089 |
|
Presentation of accounting information |
,758 |
40 |
,069 |
Source: Own elaboration.
Hypothesis testing
General hypothesis
Ha: There is a strong correlation between PBC and FS and FI in the municipalities of Lima.
Ho: There is no strong correlation between PBC and FS and FI in Lima municipalities.
Decision rule
If p< 0.05 the alternative study hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and the null hypothesis (Ho) is objected.
If p> 0.05, the alternative study hypothesis (Ha) is rejected and the null hypothesis (Ho) is accepted.
|
Table 3. General hypothesis |
||||
|
|
Control of patrimonial assets (Grouped) |
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped) |
||
|
Control of patrimonial assets (Grouped)
|
Pearson correlation |
1 |
,933 |
|
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
|
,000 |
||
|
N |
40 |
40 |
||
|
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped) |
Pearson correlation |
,933 |
1 |
|
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
,000 |
|
||
|
N |
40 |
40 |
||
Source: Own elaboration.
As shown in table 4, it is confirmed that under the Pearson correlation statistical test, there is a very strong correlation between the PBC and SF variable and the FI of the municipalities of Lima under study with a Pearson=0.933, which indicates that they have a very strong correlation; in addition, a bilateral significance of 0.000 is evident, which, according to the decision criterion, is less than 0.05, so the alternative hypothesis of the study is admitted, indicating that there is a significant relationship between PBC and SF and FI in the municipalities of Lima.
|
Table 4. Specific hypothesis 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Organization of heritage assets (Grouped) |
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped) |
|
|
Organization of heritage assets (Grouped) |
Pearson correlation |
1 |
,734 |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
|
,002 |
|
|
N |
40 |
40 |
|
|
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped) |
Pearson correlation |
,734 |
1 |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
,002 |
|
|
|
N |
40 |
40 |
|
Source: Own elaboration.
Specific hypothesis 1.
Ha: There is a relationship between the organization of heritage assets and FS and CI in Lima municipalities.
Ho: There is no relationship between the organization of heritage assets and SF and CI in Lima municipalities.
Using the Pearson correlation statistical test, it is observed that there is a significant correlation between the dimensions organization of heritage assets of the variable PBC and SF and the CI of the municipalities of Lima under study, with a Pearson = 0.734, which indicates that they have a relevant correlation; in addition, a bilateral significance of 0.002 is observed, which, based on the decision criterion, is less than 0.05, so the specific hypothesis 1 of the study is accepted, indicating that there is a relationship between the organization of patrimonial goods and the SF and the CI in the municipalities of Lima.
Specific hypothesis 2.
Ha: There is a relationship between the internal control of patrimonial assets and the FS and CI in the municipalities of Lima.
Ho: There is no relationship between the internal control of patrimonial assets and the FS and the CI in the municipalities of Lima.
|
Table 5. Specific Hypothesis 2 |
|||
|
|
Internal control of patrimonial assets (Grouped) |
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped) |
|
|
Internal control of patrimonial assets (Grouped)
|
Pearson correlation |
1 |
,812 |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
|
,001 |
|
|
N |
40 |
40 |
|
|
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped)
|
Pearson correlation |
,812 |
1 |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
,001 |
|
|
|
N |
40 |
40 |
|
Source: Own elaboration.
According to what is presented in table 5, it is evident that under the Pearson correlation statistical test, there is a strong correlation between the dimensions of internal control of patrimonial assets of the variable PBC and SF and the FI of the municipalities of Lima under study with a Pearson=0.812, which indicates that they have a relevant correlation; in addition, there is a bilateral significance of 0.001, which, based on the decision criterion, is less than 0.05, so the specific hypothesis 2 of the study is accepted, indicating that a relationship between the internal control of patrimonial assets and the SF and the FI in the municipalities of Lima.
Specific Hypothesis 3.
Ha: There is a relationship between the physical inventory and the FS and the CI in the municipalities of Lima.
Ho: There is no relationship between physical inventory and FS and CI in Lima municipalities.
|
Table 6. Specific Hypothesis 3 |
|||
|
|
Physical inventory of heritage assets (Grouped) |
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped) |
|
|
Physical inventory of heritage assets (Grouped) |
Pearson correlation |
1 |
,998 |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
|
,000 |
|
|
N |
40 |
40 |
|
|
Physical cleaning and accounting information (Grouped) |
Pearson correlation |
,998 |
1 |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
,000 |
|
|
|
N |
40 |
40 |
|
Source: Own elaboration.
Table 6 shows that under the Pearson correlation statistical test, there is a very strong correlation between the physical inventory of heritage assets dimension of the PBC and SF variable and the CI of the municipalities of Lima under study, with a Pearson = 0.998, which indicates that they have a relevant correlation; in addition, a bilateral significance of 0.000 is evident, which, based on the decision criterion, is less than 0.05, so the specific hypothesis 3 of the study is accepted, indicating that is a relationship between the physical inventory and the FS and the CI in the municipalities of Lima.
DISCUSSION
Within the range of descriptive results, in terms of the PBC variable, there is evidence of a predominance in the efficient frequency of 57.5% of the study sample; on the other hand, 37.5% have a regular level of perception concerning the variable; and 5% mention a deficient level of PBC. Likewise, concerning the dimension of organization of patrimonial assets, there is a predominantly regular level of response with 57.5%, 32.5% mentioning an efficient perception, and 10% a deficient level of response. Concerning the dimension of internal control of patrimonial assets, the following descriptive levels were obtained: 47.5% have an efficient level, 35% regular, and 17.5% deficient; finally, concerning the physical inventory of patrimonial assets, the following descriptive parameters were reconciled; 65% efficient level, 25% deficient level, and 10% regular level.
Likewise, the descriptive estimates of the respondents on the behavior of the SF variable and the IC, in this sense, concerning the SF and the IC, there is evidence of a regular descriptive behavior of 47.5% concerning the management of the variable in question, 40% favorable behavior, and 12.5% unfavorable behavior. Regarding the dimension of reconciliation of patrimonial assets, the following parameters were established: 45% favorable behavior, 32.5% unfavorable, and 22.5% regular; regarding the dimension of accounting records, 42.5% favorable, 37.5% regular, and 20% unfavorable; for the dimension of CI presentation, 70% favorable response, 25% unfavorable and 5% regular.
In this regard, it is possible to demonstrate congruence between the findings of the present investigation and those clarified by Quiroz (2022) due to inadequate control of movable assets, which inevitably leads to improper management of the city's financial data related to the reorganization of its furniture. A second similarity addressed by Romero et al. (2022) between both inquiries is the lack of clear and precise normative or directive documents to improve the administration and registration of assets, which involves all municipal agencies from the lowest levels of government to the highest (Melo et al., 2022).
On this matter, López et al. (2018) focus on determining the monetary effect of the physical, legal, and accounting improvements of the municipality on its furniture and facilities; for this purpose, they develop an integrative proposal to strengthen the efficiency, effectiveness, and efficiency of the accounting department in its management of the issue of asset control. As for the present research, it should be mentioned that the objective was not to measure the effect of inadequate asset cleaning on the municipality's finances but to determine the connection between inventory control and the accurate cleaning of furniture and other household goods. This objective was successfully met.
With a correlation coefficient of Pearson=0.933, which indicates that they have a very strong correlation; in addition, evidencing a bilateral significance of 0.000, it is clear that there is a strong correlation between PBC and FS and CI in the municipalities of Lima, this is closely related to what was clarified by Romero et al. (2022), whose results gave a very strong correlation of 0.987 from the collection established to 60 workers in the municipal area, added to this the authors mention that when the property management is rigorous, the improvement within the conciliation and internal process is better; and, to facilitate the progress of the country through the cleaning of state property, it is suggested to review the property controls (Cucat et al., 2020).
Likewise, it was evidenced that with a correlation coefficient of Pearson=0.734, which indicates that they have a relevant correlative character; in addition, with a bilateral significance of 0. 002, there is a relationship between the organization of patrimonial assets and the SF and CI in the municipalities of Lima, this in agreement with what was clarified by Anaya (2019) who established the hypothesis that there is a connection between the management of movable assets and their clean accounting was confirmed by the tests of the study, and the Spearman coefficient of 0.834 estimated indicates a strong correlation between the two variables.
With a Pearson correlation coefficient=0.812 that indicates that they have a relevant correlative character; added to this, a bilateral significance of 0.001 is reflected, demonstrating that there is a relationship between the internal control of patrimonial assets and the SF and CI in the municipalities of Lima, this by what is described by Mendoza et al. (2018), who further mention that by improving the management of the execution of public resources, the internal controls implemented by the administration will strengthen the administrative systems associated with the public expenditure cycle, leading to a better environment to formulate, approve, execute and report on the allocation or creation of public resources, when it comes to the critical processes of the organization, only intervene with units that act in everything that is directly linked to the public expenditure cycle (Urrego & Gutiérrez, 2018).
Finally, within the results, it was evidenced that with a correlation coefficient of Pearson=0.998, which indicates that they possess a relevant correlative character; added to this, a bilateral significance of 0.000 is evidenced, indicating that there is a relationship between the physical inventory and the SF and the CI in the municipalities of Lima, this in investigative agreement with what was clarified by Anaya (2019) and Laura (2017).
CONCLUSIONS
Under the Pearson correlation statistical test, a very strong correspondence between the variables PBC and SF and the CI of the municipalities of Lima under study was found with a Pearson=0.933; in addition, a bilateral significance of 0.000 was found, which showed that there is a significant relationship between PBC and SF and CI in the municipalities of Lima.
Using Pearson's correlation test, it was found that the dimensions organization of patrimonial goods of the variable PBC and SF and the CI of the Lima municipalities under study have a statistically significant correlation with each other, with a Pearson=0.734, which indicates that they have a relevant correlative character; in addition, a bilateral significance of 0.002 is evident, which showed that there is a relationship between the organization of patrimonial goods and the SF and the CI in the Lima municipalities. Under the Pearson correlation statistical test, there was a strong correspondence between the internal control of patrimonial assets dimension of the variable PBC and FS and the CI of the municipalities of Lima under study with a Pearson=0.812, which indicates that they have a relevant correlation, in addition, there was a bilateral significance of 0.001, which clarified that there is a relationship between the internal control of patrimonial assets and the FS and CI in the municipalities of Lima.
The Pearson correlation statistical test showed a very strong correspondence between the physical inventory of patrimonial goods dimension of the variable PBC and SF and the CI of the Lima municipalities under study with a Pearson=0.998, which indicates that they have a relevant correlation; in addition, a double significance of 0.000, which made it clear that there is a relationship between the physical inventory and SF and the CI in the Lima municipalities.
REFERENCES
Anaya, L. (2019). El control de bienes patrimoniales y su relación con el saneamiento contable de los bienes muebles de la municipalidad de nuevo progreso – región san martín, en el año 2017. [Tesis de grado, Universidad Nacional Agraria de la Selva, Perú] Repositorio UNAS. https://acortar.link/SfHjRq
Andara, L. y Peña, A. (2022). Presupuesto público y derechos sociales: perspectiva general sobre el cumplimiento de los derechos. Estado & Comunes, Revista de Política y Problemas Públicos, 1(14), 75-94. https://doi.org/10.37228/estado_comunes.v1.n14.2022.248
Corona, J. (2016). Apuntes sobre métodos de investigación. MediSur, 14(1), 81-83. https://acortar.link/sl9UIi
Cucat, Y., Heredia, F. y Collazos, M. (2020). Simplificación administrativa en la titulación de la posesión informal del pueblo joven Juan Pablo II en el distrito de Chiclayo. Revista Universidad y Sociedad, 12(6), 153-162. https://acortar.link/smRFbs
Gaspar, D., Soto, S. y Villafuerte, A. (2021). Control patrimonial y su efecto en la administración de bienes muebles de una institución gubernamental-2020. Ciencia Latina Revista Multidisciplinar, 5(6), 12816-12831. https://doi.org/10.37811/cl_rcm.v5i6.1285
Gómez, E. (2020). Análisis correlacional. Revista Universidad y Sociedad, 12(6), 478-483. http://scielo.sld.cu/pdf/rus/v12n6/2218-3620-rus-12-06-478.pd
Guevara, A., Espejel, J. y Hernández, J. (2018). Finanzas y gasto público en México: un equilibrio imprescindible para el federalismo fiscal. Espacios Públicos, 21(52), 83-107. https://acortar.link/p07YpF
Infantes, J. y Moquillaza, S. (2021). Implementación de un sistema integrado de planificación de recursos empresariales para mejorar la productividad en las recaudaciones por caja de una importante clínica de la ciudad de Lima. Industria Data, 24(2), 29-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.15381/idata.v24i2.19565
Laura, A. (2017). Saneamiento contable de los activos fijos y su incidencia en la calidad de la información financiera de la municipalidad distrital Coronel Gregorio Albarracín Lanchipa, periodo 2016. [Tesis de grado, Universidad Privada de Tacna, Perú]. https://acortar.link/BJMiCl
López, A., Cañizares, M. y Mayorga, M. (2018). La auditoría interna como herramienta de gestión para el control en los gobiernos autónomos descentralizados de la provincia de Morona Santiago. Cuadernos de Contabilidad, 19(47), 80-93. https://doi.org/10.11144/javeriana.cc19-47.aihg
Melo, L., Ramos, J. y Gómez, C. (2022). El presupuesto general de la nación: una aproximación a las partidas de transferencias e inversión. Desarrollo y Sociedad, (90), 153-206. https://doi.org/10.13043/dys.90.5
Mendoza, W, García, T, Delgado, M & Cedeño, I. (2018). El control interno y su influencia en la gestión administrativa del sector público Localización: Dominio de las Ciencias, (4), (4), 2018, págs. 206-24
Mendoza, W., Delgado, M., García, T. y Berreiro, I. (2018). El control interno y su influencia en la gestión administrativa del sector público. Dominio de las Ciencias, 4(4), 206-240. https://acortar.link/O62ZE0
Mite, M. (2018). Estrategias de contabilidad de gestión aplicada a pymes revisión literaria. Revista Lasallista de Investigación, 15(2), 256-270. http://www.scielo.org.co/pdf/rlsi/v15n2/1794-4449-rlsi-15-02-256.pdf
Nercesian, I., Cassaglia, R. & Morales, V. (2021). Pandemia y políticas sociosanitarias en América Latina. Apuntes, 48(89), 65-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.21678/apuntes.89.1466
Paima, R. (2018). Caracterización del control interno y la gestión de la empresa logística peruana el oriente, Pucallpa, 2016. In Crecendo, 9(4), 649-665. https://revistas.uladech.edu.pe/index.php/increscendo/article/view/2098/1500
Quiroz, J. (2022). El nivel de la gestión de la Municipalidad Provincial de Chota: Una metodología para gobiernos locales. Industria Data, 25(1), 79-102. http://dx.doi.org/10.15381/idata.v25i1.20870
Romero, R., Quispe, C., Guevara, K. y Vázquez, S. (2022). Control patrimonial y administración de bienes muebles en gobiernos locales del Perú. ECA Sinergia, 13(3), 107-114. https://doi.org/10.33936/ecasinergia.v13i3.4773
Sánchez, E. (2022). Las prácticas preprofesionales de los estudiantes de Contabilidad de un instituto superior tecnológico y su relación con la satisfacción del empleador. Industria Data, 25(1), 265-284. http://dx.doi.org/10.15381/idata.v25i1.21565
Toctaquiza, C. y Peñaloza, V. (2022). Control interno jurídico administrativo para la toma de decisión en el sector público. Dilemas Contemporáneos, educación, políticas y Valores, 9(1), 000084. https://doi.org/10.46377/dilemas.v9i.2992
Urrego, G. y Gutiérrez, J. (2018). Hacia la gestión y saneamiento financiero y fiscal de los municipios del departamento de Antioquia. Tendencias, 19(2), 113-137. https://doi.org/10.22267/rtend.181902.100
FINANCING
No external financing.
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS (ORIGINAL SPANISH VERSION)
Los autores agradecen a la Universidad Peruana Unión por el apoyo recibido para el desarrollo de la investigación.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Remilda Castañeda Ramos, Dina Arias Diaz and Abrahan Braulio Santos Maldonado.
Research: Remilda Castañeda Ramos, Dina Arias Diaz and Abrahan Braulio Santos Maldonado.
Methodology: Remilda Castañeda Ramos, Dina Arias Diaz and Abrahan Braulio Santos Maldonado.
Writing - original draft: Remilda Castañeda Ramos, Dina Arias Diaz and Abrahan Braulio Santos Maldonado.
Writing - revision and editing: Remilda Castañeda Ramos, Dina Arias Diaz and Abrahan Braulio Santos Maldonado.