doi: 10.58763/rc202211
Scientific and Technological Research Article
Resilient strategies and mechanisms of organizations to mitigate the effects caused by the pandemic at the international level
Estrategias resilientes y mecanismos de las organizaciones para mitigar los efectos ocasionados por la pandemia a nivel internacional
Johanna
Milena Mogrovejo Andrade1 ![]() *
*
ABSTRACT
Over time, pandemics have considerably affected the world economy and organizations, forcing them to generate changes and adapt. In 2019, a disease originated in Mexico, the infection caused by H1N1, which affected that country and caused illnesses and deaths. The outbreak of this disease also reached countries such as the United States, Spain, and the United Kingdom, among others. Currently, the world is on alert for a new disease growing by leaps and bounds, COVID-19, which causes high risks for organizations and international trade, staff cuts in companies and increases unemployment. Having said the above, it seeks to mitigate these negative impacts through alternatives that allow us to overcome this crisis, either through technological tools or by developing new skills. For this reason, this article aims to describe the resilient strategies and mechanisms that companies have implemented to face the adverse effects caused by the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19, international trade, crisis, pandemic, resilience.
JEL classification: O31; P33; O12.
RESUMEN
Al pasar del tiempo, las pandemias han afectado considerablemente a la economía mundial y las organizaciones, lo que las obliga a generar cambios y adaptarse. En el 2019 se origina una enfermedad en México, la infección causada por H1N1, que afectó a ese país y produjo contagios y muertes. El brote de esta enfermedad también llegó a países como Estados Unidos, España, Reino Unido, entre otros. Actualmente el mundo está en alerta ante una nueva enfermedad que crece a pasos agigantados, la COVID-19, que causa grandes riesgos para las organizaciones y el comercio internacional, recortes de personal en las empresas e incrementa el nivel de desempleo. Dicho lo anterior, se busca mitigar estos impactos negativos a través de alternativas que permitan superar esta crisis, ya sea a través del uso de herramientas tecnológicas o del desarrollo de nuevas habilidades. Por este motivo, el objetivo de este artículo es describir las estrategias resilientes y mecanismos que han implementado las empresas para enfrentar los efectos negativos causados por la pandemia.
Palabras claves: COVID-19, comercio internacional, crisis, pandemia, resiliencia.
Clasificación JEL: O31; P33; O12.
Received: 03-25-2022 Revised: 12-05-2022 Accepted: 19-07-2022 Published: 27-07-2022
Editor:
Carlos Alberto Gómez Cano ![]()
1Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander, Cúcuta, Colombia.
Cite as: Mogrovejo, J. (2022). Estrategias resilientes y mecanismos de las organizaciones para mitigar los efectos ocasionados por la pandemia a nivel internacional. Región Científica, 1(1), 202211. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc202211
INTRODUCTION
A pandemic generates a gigantic impact in the business, social and economic fields. Throughout history, pandemics have occurred without the population having time to prepare for them, since the diseases that cause them are unknown, arrive suddenly and wreak instantaneous havoc. The pandemics of the previous century caused severe economic and social disruption, as well as the loss of many lives. Something similar happened with the COVID-19 virus, which has come to significantly affect the employees of organizations, those who supply companies and customers, both in national and international companies. The pandemic restricts the ability to operate, purchase supplies and significantly reduces business opportunities, given the days of isolation that occurred as a result of this virus.
Companies are currently facing the impacts generated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has considerably altered the level of operational and strategic risk. However, it is vitally important to remain stable in order to continue contributing to the development of the economy and to fulfill their social responsibility. This consists of good corporate management to ensure the safety and proper organization of all its employees, in order to maintain stable standards of living and development.
Due to this crisis, many companies and business establishments have found it necessary to close and adapt to change, which, in turn, has led to a reduction in the production of millions of entrepreneurs. It should be noted that this presents a challenge, such as the implementation of ICT, Information and Communication Technologies, in the company's processes. In addition, the crisis has led to seek alternatives to mitigate or coexist in it, looking for economic and emotional stability that allows us to move forward and want to overcome despite the adversities that come our way. This article aims to present the main strategies applied by the business sector to mitigate these effects and seek opportunities to strengthen its ability to react to adverse situations.
METHODS
This is a reflective article and that is what its methodology consists of. It seeks to describe the strategies used by companies to mitigate the impacts of the pandemic. Thirty articles on the resilience of international trade and business were considered for the writing of this reflection. The following databases were searched: Marejadas rurales y luchas por la vida; Dialnet, Fipcaec, Revista Infométrica, Revista Electrónica Sobre Cuerpos Académicos y Grupos de Investigación; Revista Propuestas para el Desarrollo, Turismo: Estudios y Práticas (UERN), Small Business International Review, Redalyc, Económicas CUC, Scielo, Revista Integración y Cooperación Internacional, Revista Palmas, Revista Galega de Economía, among others.
Likewise, a mental map was made with the main ideas found. In the first place, the starting point was the notion of what is understood by resilience in organizations. Once this was established, the pandemic situation caused by COVID-19 was used as a basis to determine the strategies that companies could implement.
DEVELOPMENT
Background on the impacts of pandemics on the business sector and the world.
To get into context, let's start by talking about the term 'pandemic'. It is a new disease or virus that significantly affects people's lives and spreads globally. In the last century, the world has witnessed pandemics such as Asian flu, Spanish flu, Hong Kong flu, H1N1, SARS, MERS and Ebola. These have had devastating consequences on the economic system on the supply side, unexpected reduction of working life and demand, given the possibility of contagion among consumers, restrictions in the mobility of people and the inclination to save money in the face of economic uncertainty (Opertti and Mesquita, 2020).
According to Fernandez (2020), in 2003, in Guangdong, China, a disease called SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) appeared, which caused 774 deaths in 26 countries and more than 8000 infected people. The sector most affected by this virus was tourism. Surveillance controls were also carried out to identify persons with the disease. Following Vaqué et al (2009), the pandemic of the H1N1 virus, of swine origin, which appeared in Mexico in March 2009, is described. This virus continued to spread throughout the United States and the rest of the world, to such an extent that in June of that year it reached 74 countries with 30,000 cases and 145 deaths. As a result, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared a pandemic situation.
People mostly affected with this flu are in the range of 20 to 40 years of age. To prevent and control this disease, a vaccine against this virus has been prepared:
Mexico, being one of the nations with a high degree of importance in tourism, was affected in this sector, reducing the arrival of foreign tourists by 8%, businesses lost 60% of their sales, in the service sector there was a loss of almost 90%. [México al ser una de las naciones con un alto grado de importancia en el turismo se vió afectado en dicho sector reduciendo la llegada de turistas extranjeros en un 8%, los comercios bajaron un 60% en sus ventas, en el sector de servicios se obtuvo una pérdida de casi el 90%] (Vaqué et al, 2009, p. 38)
Considering WHO reports (2019), in 2012, in Saudi Arabia, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome MERS was detected, which causes shortness of breath, fever, cough and in some cases diarrhea. Mostly positive patients have presented with no symptoms. According to Monroy (2020), nearly 35% of reported cases of MERS-CoV have resulted in patient death.
Today, COVID-19 is affecting all countries and is growing rapidly. According to Garcia et al (2020), the people most prone to this virus are children, the elderly, pregnant women, people with medical conditions such as cancer, respiratory problems, heart problems and hypertension. This greatly affects populations with few medical resources unable to manage the disease.
For prevention, work is being done on social distancing, containment of the infection in medical centers and the adequate use of protection methods. According to Lugo (2020), social distancing is equivalent to physical distancing. The WHO suggests that this should be at least one meter away from the other person. All this because this virus can be easily transmitted from one person to another, "it can be transmitted from an infected patient by droplets coming out of the nose or mouth when coughing" (Europreven, 2020, p. 2).
The coronavirus crisis could surpass both the Spanish flu and the 2008-2009 financial crisis. This is due to the enormous connection that exists in the human and commercial sphere that we experience today, as a consequence of the great post-war liberalization, low transportation and communication costs and the development of global value chains.
This pandemic has significantly affected the world economy. According to Cevallos et al (2020), since the beginning of the spread of the virus, the leaders of different countries have been forced to adapt drastic measures to mitigate the impacts and generate new economic strategies. Different sectors have also been affected due to reduced consumer demand due to the spread of the virus. According to Osorio (2020), sectors such as tourism, commerce, textiles, oil, airlines, maritime and land transport have been forced to reduce their activities, which has led to liquidity being affected and staff cuts being generated.
According to a survey of exporting companies carried out by the Institute for the Integration of Latin America and the Caribbean, INTAL, of the Inter-American Development Bank, it was determined that 9 out of 10 companies in Latin America have taken measures to cushion the crisis. Some of them were opening new markets and using electronic commerce. The “survey of exporting firms in Latin America also showed that 77% of companies in America and the Caribbean decreased their intraregional exports and to the rest of the world since the start of the coronavirus pandemic” (Ibero-American Development Bank, 2020, p. 15).
A consultation carried out between May 7 and June 1, 2020, in which 532 exporting companies from 25 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean participated, showed that 77% of the companies' exports have decreased since the beginning of the coronavirus pandemic. Some results of the effects of the pandemic on international trade are presented in foreign sales, which decreased for reasons of supply and demand. One of the main causes of this decline identified by companies was the direct impact of containment measures. They also identified higher costs associated with international distribution logistics, supply chains, problems with the payment chain and delays at each stage of the production process. According to Diaz and Uparela (2020), the sector that was most affected was the services sector, given the unexpected restrictions imposed on transportation, travel, hotels and restaurants.
Continuing at the business level, according to Carpio et al (2020), many multinationals have opted to establish contingency plans or business sustainability plans that can be applied in the event of an emergency and in which risks are immediately assessed, human capital, the supply chain and customers are analyzed.
One of the best alternatives that organizations can adopt is resilience, the ability to see opportunities in the midst of crisis, to generate a minimal impact on organizations or to overcome the risks that may arise. According to Salanova (2020), resilience does not restrict us; on the contrary, it allows us to move forward despite difficulties and arises in critical situations.
Examples of companies that have sought alternatives to survive in the midst of the crisis
As previously mentioned, the coronavirus pandemic has been devastating for the world economy. However, all the measures of confinement or quarantine have influenced some companies to progress, mostly those that manage everything in the virtual field. It is even to be admired and congratulated those success stories of businesses that, when affected by the crisis, have overcome and risked the use of electronic commerce.
According to BBC News (2020), some examples of them are companies such as Amazon, Netflix, Disney, among others, which, in the first quarter of 2020, due to COVID-19, had a boom in their sales and subscriptions. This is explained because most people chose to stay at home and spend more time with their families. The problem that plagues after the increase in demand and abrupt confinement is a slowdown in the production of movies and series, as was the case with Netflix.
According to Ventrici et al (2020), technology-related companies have positioned themselves and have had high growth in COVID-19 time. These organizations are market leaders and show an increase in sales. An example of this can be found in Argentina, with two large companies such as Mercado Libre and Globant, which had a high growth of 37% and 17% respectively.
It should be noted that some companies and factories, after being affected, are forced to seek alternatives to survive or remain in the market in the midst of this pandemic. According to García et al (2020), one of them is the implementation and use of new technologies, making drastic adjustments in global supply chains and adapting to what will be a new world. What today is seen as a crisis will in the future be seen as opportunities for companies.
Due to the time elapsed of the pandemic and the prevention used to avoid any type of contagion, many companies have made changes in their manufacturing process, providing innovation to what is lived today. According to Matallana (2020), it is important to reinvent oneself, to offer new products and services from what was being worked; to take risks, but always taking care of the target market; somehow shortening the distance that exists with the customer. Another key component is quality and added value; without leaving aside or forgetting technology in each of the procedures implemented in the company.
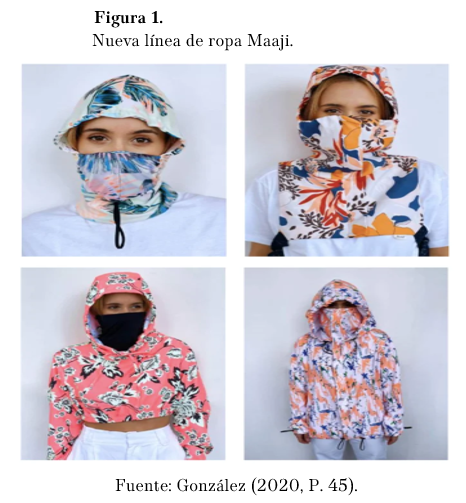
According to the newspaper El Tiempo (2020) MAAJI is a company dedicated to the manufacture, distribution and marketing of swimwear, in times of pandemic opted for a new line called "protective wear", which consisted in the manufacture of protective garments against contagion, as masks, jackets, pants, special hoods, all with unique styles and using biosafety standards.

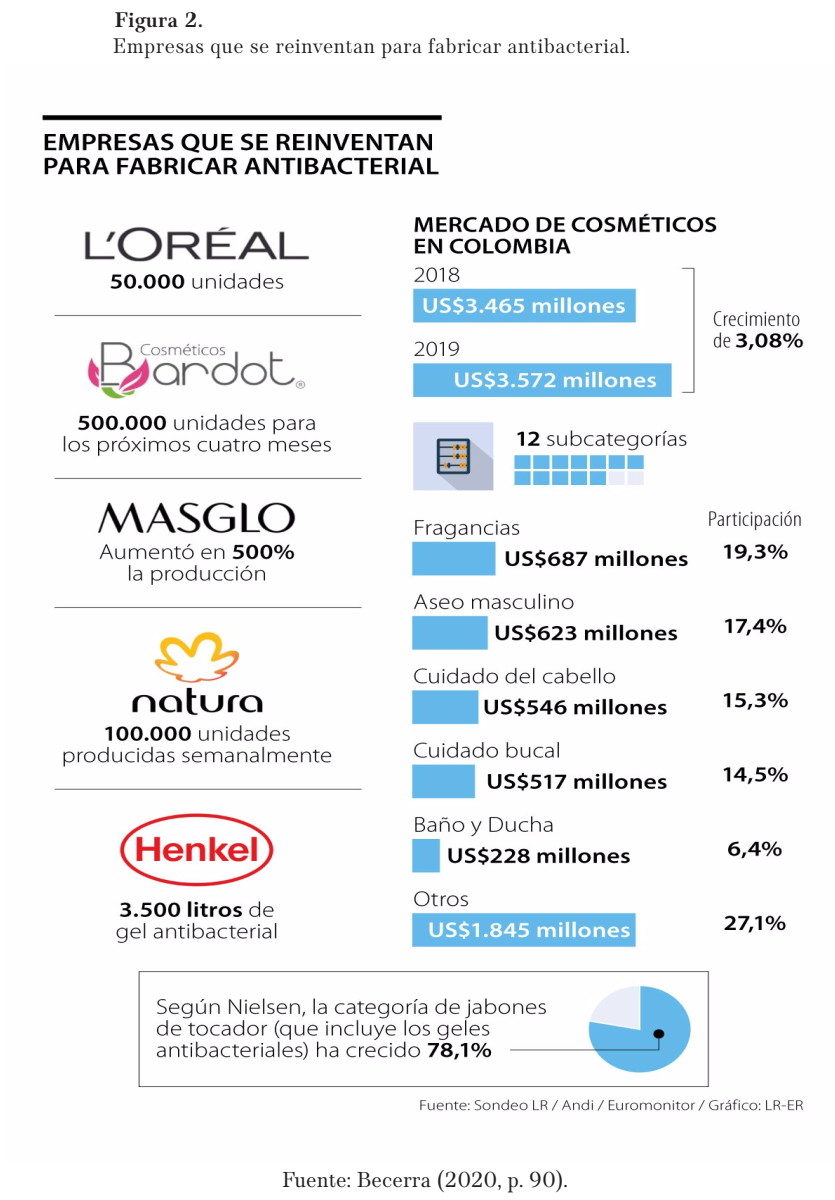
According to Becerra (2020), several cosmetic companies have also reinvented themselves and have included antibacterial gels in their manufacturing process. The beauty and cosmetics multinational L'Oreal started manufacturing 50,000 units for medical centers, personnel and customers.
Another company facing the challenge of surviving the coronavirus is the Bacardi rum distillery, especially given the unexpected closure of bars, nightclubs, among others. In this context, the distillery has opted for the implementation of strategies that will allow it to continue growing in the market, among them, creating low-alcohol beverages that allow people to drink them at home in a more relaxed way and with their families. It is also reinventing itself in e-commerce in the United States and Europe.
According to Velazco (2020), Bacardi and Olein Refinery are joining forces to produce more than 1.7 million hand sanitizers, much of it donated to police, firefighters, among others. In Bacardi's 158 years, the company has weathered difficult times and has understood that, in order to be strong in the market, it is necessary to be resilient and positive in the face of any circumstance.
On the other hand, in terms of innovation and struggle, in this process against COVID-19, according to the newspaper El Universal (2020), Engineer Andrés Ramírez, from the Faculty of Engineering of the Universidad de la Sabana, with the support of other engineers, developed a Mechanical Ventilator, which consists of mechanically assisting pulmonary ventilation when it is ineffective. The group delivered its patent to the Military Industry, in order to save many lives in the middle of the pandemic.

Like these, many other companies have chosen to implement strategies to help mitigate the negative impacts of this pandemic and respond to this crisis that, in one way or another, has caused a reduction in sales.
RESULTS
According to the information in this article, it is evident that companies worldwide focused on designing strategies according to the effects of the pandemic in each sector of the economy and society. The strategy with the best performance is the use of e-commerce or electronic commerce. This medium has become indispensable to continue the operation processes of any type of company, as it is the ideal way at this time to establish communication with employees, customers, suppliers and the financial sector.
Secondly, we find the reinvention of processes through the implementation of strategies to efficiently carry out supply and distribution chains, production and resource management to generate profits that ensure the survival of the company and its personnel.
Another of the strategies proposed is the opening of new niches and market lines, to take advantage of the current demand for prevention, protection and care products against the virus. This situation has led companies and brands to start new products in their offerings, for example, manufacturers and distributors of swimwear opened a line of specialized anti-fluid suits.
On the other hand, there are marketing strategies that can be included in strategic planning, mainly to face markets in crisis. These can be implemented by companies to mitigate or strengthen their business competitiveness. As it is a phenomenon that can be predicted with little precision, especially in terms of duration, the crisis becomes an element that should be included as a probable occurrence in business scenarios. Therefore, it is necessary to generate adequate planning in the event of a crisis in the markets in which it participates or even in industries that influence its competitiveness.
According to the study conducted by Osorio (2020), in Colombia, companies such as Crepes & Waffles, whose founder is Beatriz Hernández, encouraged their employees, all of them mothers, to stay at home without sacrificing their salary. The food they kept in their refrigerators was also sold at very low prices. In addition, with the extension of the quarantine, this company found it necessary to reinvent itself in the marketing of its products, for example, through the sale of its menu so that its customers could prepare it at home.
Another case was that of Arturo Calle. This company closed its stores, but did not stop paying its workers, as its owner announced: "The human being above money". Almacenes Only, a company of Bogota tradition and one of the most recognized businesses in the region, whose sales were only in physical stores, reinvented itself and transformed to a new mechanism of home sales, which is coordinated through the WhatsApp social network.
However, companies have not been the only ones to establish measures to cushion the effects of COVID-19. The governments of each country, due to the pandemic, must be in constant analysis to establish measures to protect their population and strategies to cushion the economy of nations in the face of the crisis and reduce as much as possible the devastating effect on society.
DISCUSSION
"A resilient organization is one that not only survives over the long term, but also flourishes, standing the test of time." (Kerr, 2020, p. 45). With this crisis it is worth noting that humanity is in the process of reinvention and individual transformation, to achieve and maintain results that will help its family, social and organizational nucleus to cope and adapt to all the changing circumstances in this process.
COVID-19 has not only affected people's physical and mental health, but also the world economy. According to Osorio (2020), during these first months of the year, the spread of the virus has been exponential, which has led the leaders of the countries to take measures for its mitigation and to rethink the necessary steps to apply new economic strategies.
The impact on each of the sectors is affected by consumer demand, which is decreasing as the virus spreads. Sectors such as oil, tourism, commerce, textile, airlines, maritime and land transportation have had to reduce their activities, which has affected liquidity. For this reason, many companies have had to make personnel cutbacks, hand over offices, liquidate contractors, among other decisions, in order not to increase their economic obligations. For other sectors, such as the stock and financial markets, the impact was reflected in the fall of the London, Wall Street and Nikkei stock exchanges in Japan, among others. Consequently, since the beginning of the outbreak in December, banks in each of the countries took measures such as interest rate reductions and grace periods to cushion the economy.
We cannot forget the education sector, which has not ceased operations thanks to the commitments of its educators. However, the reactivation of the economy will not happen soon and the impact will be greater, since parents will not be able to pay tuition and pensions and their liquidity will decrease. Likewise, sectors such as health and pharmaceuticals have been the beneficiaries in this time of crisis, since companies such as Johnson & Johnson (J&J), Glaxosmithkline and Sanofi recorded advances in their drugs against the virus. According to Osorio (2020), at least two of them officially announced their collaboration in the development of the vaccine and affirmed their capacity to manufacture enough to partially cover the world.
In the same line, the generation of employment in health entities has increased since the appearance of the virus. This increase was not only in jobs such as doctors and nurses, but also in cleaning, parking, security and customer service staff, among others. Likewise, the trade of care and protection implements such as antibacterial gels, alcohols, anti-fluid suits, masks, mouth masks, respiratory equipment, gloves, disinfection elements and all other elements necessary in intensive, palliative and hospital care also grew.
Currently, studies have shown the mutation of the virus and its resistance to drugs, which leads each of the companies and governments to learn to live with it. To this end, they generate economic and social strategies in the face of this disease, among which is the rethinking of their visions and missions for the generation of income, since during these months the supply of products has been widely managed from virtual platforms.
According to Xifra (2020), the Covid-19 crisis is affecting internal communication in companies, due to the change of technological tools among employees that had never been implemented before. Technologies such as SaaS (software as a service) that has favored online education platforms. Another element under the implementation of ICT and that allows us to work remotely are applications such as Gmail, Google drive, Google docs, Google apps, Meet, among others.
Many companies around the world have responded positively to the current crisis, which can be seen in their efficient management of the individual and collective needs of the company and its employees, the latter being a fundamental and essential part of a renewal and coping with the crisis.
Based on the pandemic situation, a new distribution landscape has emerged, as it is evident that digital channels have been the major players and, together with the search for spaces that are safe, will set the trends for the coming months or even years.
According to Resa (2020), the increase in online shopping that is currently being experienced is requiring retailers to improve their relationships with their customers. These changes present challenges in retail establishments, which strikes a balance between selling physically and virtually thereby withstanding the crisis. This has led companies to create strategies to attract shoppers and create a facility to manage their orders quickly and efficiently.
CONCLUSIONS
Given the current crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the work of governments and emergency services is focused on meeting immediate needs such as hunger, protecting families, increasing hospital capacity, protecting businesses from eviction and bankruptcy, and protecting employees and their families. Much of the funds used for the above-mentioned objectives come from agencies such as the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, regional development banks and central banks.
Similarly, some countries are already in the process of developing preliminary strategies to begin the recovery phase. The role of public administrations will be to boost demand, provide substitute income and attract new investments. The recovery phase is expected to generate prosperity and develop the resilience of people and markets to withstand the different external crises that may arise, recover and strengthen, as well as contribute to the growth of the countries' potential and their proper development, in order to achieve long-term sustainability.
At this time, companies are forced to deal with various strategic and operational challenges such as changes in demand trends, delays or interruptions in the supply chain, delays in the shipping logistics chain, increased costs, as well as the protection of employee health and safety or complications in export and import issues.
Today, as most countries are in the process of coping with the pandemic crisis, it is vitally important that companies, as key players in the economy, perform excellent business management, as well as ensure the safety and health of their employees.
This is why organizations must reinvent themselves to adapt to new trends and market needs, including within their strategies digital marketing, E-COMMERCE, improving their production processes, among others, in order to remain competitive and contribute to the recovery of their environment.
REFERENCES
Banco Iberoamericano de Desarrollo (2020). 9 de 10 empresas han tomado medidas para amortiguar el impacto de la pandemia. https://acortar.link/XHP3Ph
bbc News. (2020). La economía y el coronavirus: los negocios ganadores y los sorpresivos perdedores durante la pandemia. https://acortar.link/eHlkvs
Becerra, L. (4 de mayo de 2020). L’Oréal, Masglo y Bardot, entre las empresas que ahora producen gel antibacterial. La República. https://acortar.link/3ZIMWE
Carpio, D., Martínez, M., Salgado, A., Daponte, S., Díez, R., Castro, E., Fernández, E., Pérez, P. y Turnes, J. (2020). Efectividad del plan de contingencia de la unidad de enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal ante la infección de Covid-19. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública, (94), 273-298. https://acortar.link/GjWBJR
Cevallos, K., Bermeo, K. y Vásconez, L. (2020). Covid-19 y su impacto contable en las PYMES del cantón Cuenca. Revista Arbitrada Interdisciplinaria Koinonía, (5), 273-298. http://dx.doi.org/10.35381/r.k.v5i4.958
Diaz, I. y Uparela, R. (2020). COVID-19 y sus posibles efectos en los negocios internacionales [trabajo de grado]. Universidad de Córdoba, Colombia. https://acortar.link/Qq8AyQ
El Tiempo. (23 de abril de 2020). La empresa de bikinis y las 40 más que se reconvirtieron y son éxito. El Tiempo. https://acortar.link/m1lFZP
El Universal (2020). El ingeniero cartagenero que hace historia en la lucha contra el covid. El Universal. https://acortar.link/k4faMC
Europreven (2020). Medidas de prevención frente al covid-19 en empresas. https://acortar.link/6bIFpf
Fernández, F. (2020). Estudio de impactos de pandemias del siglo XXI en la economía y el sector turístico [Tesis de pregrado]. Universidad de la Laguna, España.
García, C., Pérez, B. y Navarrete, M. (2020). Las empresas ante el COVID-19. Revista de investigación en Gestión Industrial, Ambiental, Seguridad y salud en el Trabajo – GISST, 2(2), 85-101. https://doi.org/10.34893/gisst.v2i2
García, G., Linares, O. y Proenza, L. (2020). Prevención de COVID-19 en pacientes del Policlínico René Vallejo Ortiz. Revista científica estudiantil 2 de Diciembre, 3(2), e60. https://acortar.link/EdaK06
González, T. (2020). La colombiana Maaji presenta una nueva línea de moda para protegerse del coronavirus. Fashion Network. https://acortar.link/Sxn73Y
Kerr, H. (2020). bsigroup. https://acortar.link/D7TCCi
Lugo, V. (2020). La pandemia COVID-19, distanciamiento social, el uso de tecnologías de la información y comunicación y la falta de regulación internacional que proteja los datos personales [trabajo de grado]. Universidad La Salle, México. https://acortar.link/C0gSVE
Matallana, L. (2020). Retos Empresariales Tras el Coronavirus COVID 19 [trabajo de grado]. Universidad Católica de Colombia, Colombia. https://acortar.link/cvRX09
Monroy, J. (2020). Efectos de los coronavirus del síndrome respiratorio agudo grave (SARS-CoV) y del síndrome respiratorio del medio oriente (MERS-CoV) en el sistema nervioso. ¿Qué esperar del SARS-CoV2? Revista Biomédica, 40(Supl. 2), 173-179. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.5682
Opertti, F y Mesquita, M. (26 de marzo de 2020). Impacto del coronavirus en el comercio y la integración: ¿qué hacer? Forbes Centroamérica. https://acortar.link/Yjfhoa
Organización Mundial de la Salud (oms). (2019). Coronavirus causante del síndrome respiratorio de oriente medio (MERS-Cov). https://acortar.link/qehf7x
Osorio, L. (2020). La resiliencia como opción para superar la economía en medio de las pandemias [trabajo de grado]. Universidad Católica de Colombia, Colombia. https://acortar.link/8cf46I
Resa, S. (2020) ¿Cómo evoluciona la distribución comercial tras la pandemia? Distribución y Consumo, 2, 43-51. https://acortar.link/ibEp0j
Salanova, M. (2020). How to survive COVID-19? Notes from organisational resilience (¿Cómo sobrevivir al COVID-19? Apuntes desde la resiliencia organizacional), International Journal of Social Psychology, 35(3), 670-676, https://doi.org/10.1080/02134748.2020.1795397
Vaqué, J., Gil, J. y Brotons, M. (2009). Principales características de la pandemia por el nuevo virus influenza A (H1N1). Medicina Clínica, 133 (13), 513-521. https://acortar.link/EdaK06
Velazco, J. (26 de marzo de 2020). Bacardí elabora desinfectante de manos y lo dona para luchar contra el coronavirus. https://acortar.link/758bp7
Ventrici, P., Krepki, D. y Palermo, H. (2020) Sector software y la situación respecto de la pandemia de COVID-19. https://acortar.link/ogXE1f
Xifra, J. (2020). Comunicación corporativa, relaciones públicas y gestión del riesgo reputacional en tiempos del Covid-19. El profesional de la información, 29(2), e290220. https://doi.org/10.3145/epi.2020.mar.20
FINANCING
No external financing.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS (ORIGINAL SPANISH VERSION)
Se agradece a la Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander por el apoyo recibido.
AUTHOR'S CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Johanna Milena Mogrovejo Andrade.
Research: Johanna Milena Mogrovejo Andrade.
Methodology: Johanna Milena Mogrovejo Andrade.
Writing - original draft: Johanna Milena Mogrovejo Andrade.
Writing - revision and editing: Johanna Milena Mogrovejo Andrade.