Review Article
Management skills as a factor of business competitiveness
Habilidades gerenciales como factor de competitividad empresarial
Diana Esther Álvarez Contreras1 ![]() *, José David Montes Padilla1
*, José David Montes Padilla1 ![]() *, Cristian
David Osorio Martínez1
*, Cristian
David Osorio Martínez1 ![]() *
*
ABSTRACT
Managerial skill is a crucial factor in the formation and performance of effective leaders. This capability fosters strategic alignment in organizational management, especially in adapting to market changes, which has driven new ways of managing, controlling, executing, assessing, and making decisions to achieve operational and mission-related objectives in companies. This article sought to analyze the importance of managerial skills as a key element of business competitiveness. A descriptive qualitative approach was used, drawing from freely accessible electronic documents. The results focus on three main themes: managerial skills as a competitive strategy, fundamental skills of a manager for business competitiveness, and managerial skills as a factor of competitiveness. The findings suggest that companies increasingly require management staff with knowledge, experience, and skills that allow them to achieve objectives and business success. Managerial prowess is, therefore, an essential aspect to foster competitiveness in the corporate realm.
Keywords: business management, professional competence, competitiveness, vocational training.
JEL Classification: J24; L29; M19.
RESUMEN
La habilidad gerencial es un factor crucial en la formación y desempeño de líderes efectivos. Esta capacidad genera una alineación estratégica en la gestión organizacional, especialmente en la adaptación a los cambios del mercado, lo cual ha impulsado nuevas formas de administrar, controlar, ejecutar, evaluar y tomar decisiones para alcanzar objetivos operativos y misionales en las empresas. Este artículo buscó analizar la importancia de las habilidades gerenciales como elemento clave de la competitividad empresarial. Se utilizó un enfoque cualitativo descriptivo, recurriendo a documentos electrónicos de libre acceso. Los resultados se centran en tres temáticas principales: las habilidades gerenciales como estrategia competitiva; habilidades fundamentales del gerente para la competitividad empresarial; y habilidades gerenciales como factor de competitividad. Los hallazgos permiten concluir que las empresas, cada vez más, requieren personal directivo que no solo cuente con conocimientos y experiencia, sino también con habilidades que les permitan alcanzar los objetivos y el éxito empresarial. La destreza gerencial es, por lo tanto, un aspecto esencial para fomentar la competitividad en el ámbito corporativo.
Palabras clave: administración de empresas, competencia profesional, competitividad, formación profesional.
Clasificación JEL: J24; L29; M19.
Received: 27-04-2023 Revised: 20-05-2023 Accepted: 15-06-2023 Published: 04-07-2023
Editor: Carlos
Alberto Gómez Cano ![]()
1Corporación Unificada Nacional de Educación Superior – CUN. Sincelejo, Colombia.
Cite as: Álvarez, D. Montes, J. y Osorio, C. (2023). Habilidades gerenciales como factor de competitividad empresarial. Región Científica, 2(2), 2023109. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc2023109
INTRODUCTION
Managerial models have been updated with the passage of time marked by the development of economic processes (de Almeida et al., 2021), competitiveness and technological development (de Andrés-Sánchez et al., 2022; Sehnem et al., 2020), enhanced by the need to optimize product quality and the changing environments of increasingly dynamic markets (Hu, 2023; Munastiwi, 2015), based on the present and nascent skills that managers possess (Oppong & Segbenya, 2023; Heubeck, 2023), aimed at responding to, as well as continuously improving organizational processes and providing in their management (Elia et al., 2022), skills that enable companies a competitive advantage and representativeness in the market (Suriaga & Gamboa, 2019). Therefore, the role of a company in the market and its efficient management depends mainly on the managers or administrators and the skills for implementing their business.
In addition, managerial skills are a vehicle for skills transfer, through which the managerial human talent raises strategic actions and puts into practice the administrative tools for the company's success (García et al., 2017). For this reason, the manager must be equipped with the competencies (Gao et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2019), skills, disciplines, and knowledge that allow him/her to solve problems, generate new positive experiences and benefits for the company (Gunawan et al., 2023; Lee et al., 2021).
However, the reality of management practice in companies shows that it goes beyond theory since practice proves to be more demanding. It is worth mentioning that many managers and leaders fail or show problems when facing and anticipating changes in the environment (Su et al., 2023); this context has increased the need for managers to develop skills that allow better performance; for this reason, knowledge of managerial skills motivates the development of knowledge management in order to create basic strategies for the consolidation of organizational culture (Ferrando & Callohuanca, 2020).
These qualities are often not consolidated during professional training (Martínez et al., 2020). In this sense, a manager, with the qualities and fundamental qualities, will be a guarantee to take advantage of opportunities in the business field and to face with determination the barriers (nature of the companies, competitiveness, innovation, among others), which may prevent its evolution in the market. In this order, this article aims to analyze the importance of managerial skills as a factor in business competitiveness.
METHODS
The research has a qualitative, descriptive approach. The empirical method used was the literature review. For this purpose, different open-access databases were used, such as SciELO, Redalyc, Latindex, and open-access journals indexed in Scopus and WoS. The search strategy was established according to the central themes of the analysis: management skills as a competitive strategy, fundamental managerial skills for business competitiveness, and management skills as a factor of competitiveness. In addition to the above, the documents were selected based on the following inclusion criteria:
a) originality of the writings;
b) years of publication (2001-2021), with the exception of (Katz, 1974) whose relevance is timeless; and
c) relevance to the topic of analysis.
RESULTS
Management skills as a competitive strategy
The economic development of a country is directly related to the stability, growth, and innovation processes of companies (Handayani & Er, 2019), which, despite market changes, have, for the most part, the ability to respond adequately to the difficulties of the environment (Wang et al., 2023); while others tend to disappear due to the absence of good management decisions and practices. It is necessary to be competent and competitive in an increasingly globalized environment (Qian et al., 2023).
Consequently, managers must develop managerial skills to respond appropriately to changes to achieve the organizational objectives (sustainability and profitability). In this regard, Ibarra et al. (2017) highlight the influence of institutional policies and organizational culture in increasing productivity and its correlation with increased competitiveness. Faced with this aspect, the evolution of the company will be due to good management and manager performance (Fan et al., 2023; Wang & Cao, 2022), conditions that make the difference.
Thus, competitiveness is positively impacted by the use of managerial skills (Pedraza et al., 2023; Sambasivan et al., 2009), which allows him/her to make decisions appropriately, generate strategies, creatively solve labor and market difficulties, establish contractual relationships to enable an optimal organizational climate and to develop, at the same time, empathy, assertiveness and emotional regulation, through which companies create and sustain in the long term an added value to their organizational mission and vision (Sarwar et al., 2023; Bruno et al., 2023).
Therefore, in the organizational context, a manager's contribution is fundamental since it provides mandatory tasks for the correct management and the use of all his knowledge and potential in the administrative, planning, organization, direction, and control processes. This implies developing specific skills to develop the duties and activities inherent to their position, whose leadership is determinant in the consolidation and execution of organizational processes (García et al., 2017). However, leadership is currently expressed as a challenge.
This is the most critical skill of an individual within an organization since it promotes interaction, cooperation, and strengthening of companies not only in their environment but also in a broader scope, such as markets. Therefore, managerial skills are born of broad administrative thoughts, identifying management as the process of planning, coordination, direction, and control of activities to achieve the objectives set (Sanchez, 2016).
From these, attitudes and knowledge are forged to respond positively to market changes (Schöck et al., 2023; Suh et al., 2012). In addition, it is vitally important to emphasize that this new knowledge is incorporated into old knowledge to generate, on the one hand, more excellent responsiveness and decision-making power and, on the other hand, to enable the organization to possess suitable intellectual capital adjusted to the variables of its environment.
Intellectual capital is an essential resource for organizational development since it facilitates meeting the company's needs. This implies that intellectual capital, despite its intangibility and immaterial nature, can create benefits in organizations, which are generated through its management, development, and execution (Barrios, 2017). The task of the manager-administrator is a challenge since the proper functioning and benefits for the company will depend on his decisions.
However, leaders must develop new ways of demonstrating managerial skills to strengthen and evolve in other areas since expertise will allow them to overcome positive or negative situations in management to maintain the quality of the processes (Naranjo, 2015). According to this author, the business environment is subject to constant changes, which is unpredictable and affects the decisions of the moment, since they can benefit the company but also affect the projections and its future development; from his perspective, it is proposed to train committed managers (Kang et al., 2023; Lee & Aghamohammadi, 2023; Donnelly et al., 2023), with skills and knowledge that respond effectively to the incidences provided by the environment, in order to generate business stability, without leaving aside the desire and need for growth of the organization.
On the other hand, it is essential to highlight that business competitiveness is the result of the combination of good management, human capital, skills, and attitudes that effectively impact business management. This can be determined through the applicability and use of management tools such as indicators that are key in the dynamics of the organization (Alghamdi & Agag, 2024; Barba-Aragón, 2014). In other words, these tools help to specify the decision-making and strategies that the manager advances in his management; at the same time, they strengthen his participation in a successful way in the face of changes in the environment, transforming comparative advantages into competitive ones (Bergin, 2022; Candau et al., 2022).
It is worth mentioning that in order to be competitive, companies must not only have the best production and management practices but also have a balanced environment in which aspects such as infrastructure, corporate culture, knowledge management, and environmental management gain value (Ibarra et al., 2017). Given the above, information and knowledge are strategic variables of competitiveness in organizations. Today, the economy highlights human capital as an indicator of effectiveness in the performance of companies; managers and their collaborators represent the basis for growth in each organization so that continuous learning and innovation can take place and so that the intangible assets of competitive advantage can be strengthened in parallel (Delfín and Acosta, 2016).
Key managerial skills for business competitiveness
Managers' business management involves using their potential and developing essential competencies and skills to promote good performance and estimated results in which qualities such as communication, creativity, security, self-control, empathy, negotiation skills, and critical thinking, among others, take precedence. In the current business context, managerial skills become organizations' most important knowledge and assets (García et al., 2017). These aspects highlight the importance of developing and generating growth in people, where their potential and professional profile are deployed. In this regard, Cantillo (2017) expresses:
A professional stands out in the fact that he/she can demonstrate the mastery of personal, ethical, and moral skills that have a positive impact on the fulfillment of the activities inherent to his/her professional practice and those required by the employing company, as well as the development of thinking skills [Un profesional, entre las cuales sobresale el hecho de que pueda demostrar el dominio de habilidades personales, éticas y morales que repercutan de manera positiva en el cumplimiento de las actividades inherentes a su ejercicio profesional y a las requeridas por la empresa empleadora, así como en el desarrollo de destrezas del pensamiento] (p. 78).
In this sense, professionals at the head of companies or organizations must have the capabilities, competencies, and skills necessary to exercise their profession and business practice; these, in turn, transcend benefits, competitiveness, and profitability. Today's companies require suitable managerial capital, capable of facing changes and seeking alternatives that allow them to stand out from the competition and that their internal structure is balanced, i.e., a manager who knows his potential and uses it for the benefit of the organization (Montoya & Boyero, 2016).
On the other hand, there are many skills or competencies that the manager or company leader must develop to motivate, delegate, inspire, and transmit values to his collaborators. This allows him/her to perform in the business and implement actions that favor productivity and competitiveness in the changing environment (Arrascue et al., 2021). It is essential to highlight that the skills that a person exhibits, especially professionals in management or administrative areas, are derived from those competencies for life that allow them to have a healthy, realistic, optimistic, and persevering existence in the face of life. In this sense, the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1999 and the United Nations Children's Fund (Unicef) in 2017 highlight the following skills: cognitive, emotional, and social.
These skills promote coherent and assertive behavior in the human being, who, with judgment and responsibility, can assume each decision in his daily life. In addition to the above life skills, the manager must develop the following, which, according to Magdaniel et al. (2016), are adequate to face the market and global demand: "strategic thinking, creativity, planning, coordination of actions, motivation, leadership, conflict management, teamwork, and decision making" (p. 135). It is worth mentioning that each one is important to the extent that the manager makes proper use of them since they are of more significant benefit in actions involving his performance and the relationship with others.
In this sense, Katz (1974) enunciates the essential managerial skills for managers' efficient and successful exercise (Figure 1). While Whetten and Cameron (2011) identify a group of essential skills for personal and organizational success (figure 2).
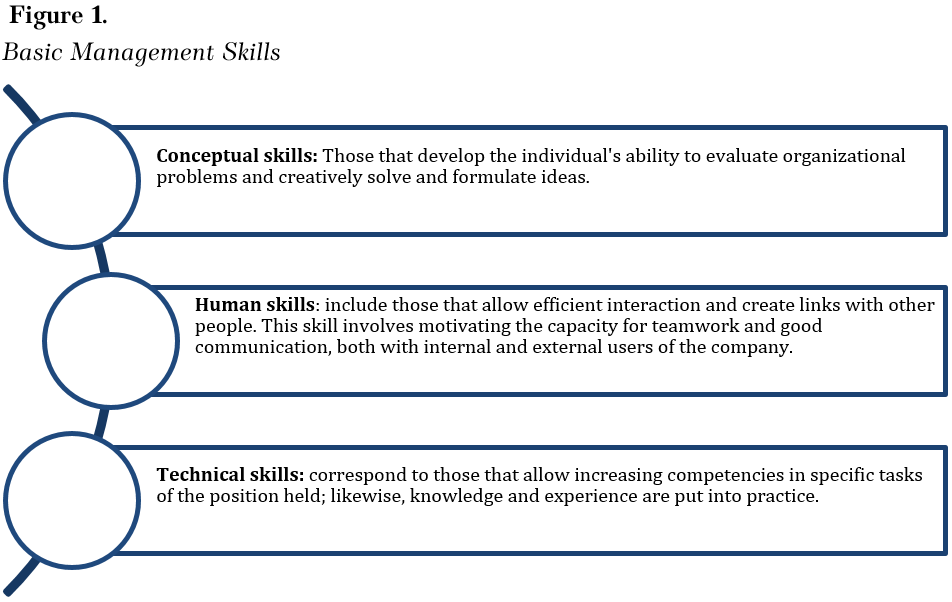
Source: Own elaboration based on Katz (1974).

Source: Own elaboration based on Whetten and Cameron (2011).
Essential skills refer to the recognition of oneself and the assumption of the impacts of one's work performance, through which good behavior and transformation in interaction with other members of the organization are promoted. These relationships improve the work environment and the achievement of goals. Hence, the manager, leader, or director of a company, in order to obtain optimal results in the business, requires aspects that help to consolidate his management (knowledge - experiences), as well as to know himself and develop conceptual, technical, and human skills that allow a good performance and development of strategic tools that promote the fulfillment of the objectives in the organization and improve its representativeness in the market.
Management skills as a factor of business competitivenes
Nowadays, the knowledge of top management and strategies are fundamental tools to achieve business success because, with them, it is possible to face changes in the environment efficiently; that is, it is possible to analyze the impact of the production, marketing, and distribution of a product. In the same way, it is possible to determine how a service has been provided and the relationships with the organization's internal and external customers.
Therefore, from management, each organization establishes strategic plans that result from profitability and competitiveness. Companies of all types must be prepared for changes (Martínez et al., 2017). That is, management must create, implement, evaluate, and enhance skills aimed at promoting the efficiency of human resources, which could be said to automatically commit to helping meet the company's mission and operational objectives.
This creates an integrated work environment, generating sustainable and lasting advantages over time. According to García et al. (2017), every company's objective is to achieve its operations' effectiveness with positive results that allow it to differentiate itself by defining strategies focused on achieving competitive advantages. The authors propose that management agrees on unique strategic forms that are challenging to imitate in its environment, producing a high differentiation of its economic activity.
It is also worth mentioning that management skills are a determining factor in business growth since they direct the behavior and capacity of human talent to manage a workgroup or a company with effective results. Likewise, the manager foresees the company's competitive approach and the possible scenarios that may be faced in the short, medium, and long term. In this sense, management focuses on generating strategies based on their skills to achieve optimal performance of the organization, according to principles of planning, direction, and control of the process to be executed. These strategies are established in response to the company's competitive environment.
Table 1 shows an analysis of research results reflecting skills and their influence on competitiveness, regardless of the company or type of business.
|
Table 1. Research on skills and their influence on competitiveness |
||
|
Titulo |
Autor (año) |
Resultados |
|
The managerial skills that SME entrepreneurs in the city of Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico (Habilidades gerenciales como estrategia de competitividad empresarial en las pequeñas y medianas empresas (Pymes)). |
Leyva et al. (2017) |
Companies in Hermosillo-Sonora, in order to achieve sustained advantages in the market and business competitiveness, require a dynamic, updated management, with operational and management skills, strategic administration, strategic planning, globalization and human resources, always open to organizational and technological change. |
|
Management skills that enable the competitiveness of agribusinesses in the Mexicali Valley, Mexico. |
González y Ley (2019) |
The authors indicate that it corresponds to short and medium-term strategic planning, the manager's capabilities and knowledge for the achievement of business objectives. |
|
Strategies and skills for competitiveness: the case of SMEs in the construction sector in Barranquilla |
García et al. (2019) |
They point out that managers of construction companies develop management skills in a moderate way (conceptual, technical and human), which is reflected in the lack of activities for the development of strategies and the promotion of work efficiency in their collaborators, teamwork, good communication and leadership are encouraged, generating trust and a positive dynamic in each of the activities. |
Source: own elaboration
Therefore, management skills as a factor in business competitiveness are determinant since they contribute, from the exercise of management to facing the changes and challenges of the internal and external environment of the company and managing in advance the actions to be developed to obtain better efficiency and participation in the market. In this sense, the current goal is to be sustainable over time and, thus, to be difficult to imitate by the competition, especially in these business dynamics characterized by uncertainty and complexity of the environment; hence, the need for a manager with a creative, innovative, dynamic mentality, open to technological and organizational changes.
CONCLUSIONS
With the constant changes in the business environment and its dynamization, the manager has been empowered to adopt and exploit new skills aimed at improving organizations, positively impacting the achievement of its objectives, adopting management skills in each employee of the company, and generating competitive administrative processes. From these elements, the organization is given a more significant presence in markets nationally and internationally. For this, it is essential to have a person at the management level with the ideal profile, adequate knowledge, and skills who responds effectively to business activity's changing times and uncertainty.
However, it is essential to mention that, together with the manager, there must be collaborators who comply on equal terms so that this has an impact on teamwork, synergy, and empowerment. This promotes an excellent organizational climate and the desired business competitiveness.
Future work should focus on determining key variables that describe primary managerial skills and business competitiveness, allowing the development of statistical tests of correlation between variables and the determination of dependence-influence relationships.
REFERENCES
Alghamdi, O. y Agag, G. (2024). Competitive advantage: A longitudinal analysis of the roles of data-driven innovation capabilities, marketing agility, and market turbulence. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 76, 103547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2023.103547
Arrascue, I., Podestá, L., Matzumura, J., Gutiérrez, H. y Ruiz, R. (2021). Habilidades gerenciales desde la percepción del personal en el Hospital Municipal los Olivos. Revista Facultad de la Medicina Humana, 21(2), 275-282. http://dx.doi.org/10.25176/rfmh.v21i2.3715
Barba-Aragón, M. (2014). La habilidad de los directivos y su papel mediador entre formación e innovación. Revista Europea de Dirección y Economía de la Empresa, 23(3), 127-136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redee.2014.03.001
Barrios, R. (2017). El capital intelectual como recurso generador de competitividad en las organizaciones. Revista Ensayos, 10(10), 96-103. https://revistas.unal.edu.co/index.php/ensayos/article/download/72498/66248
Bergin, P. (2022). Currency undervaluation and comparative advantage. European Economic Review, 150, 104316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroecorev.2022.104316
Bruno, G., Guerrini, G. y Caballini, C. (2023). The use of the CTU Code to increase freight transport safety and business competitiveness: An empirical analysis of a sample of Italian companies. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, 19, 100826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trip.2023.100826
Candau, F., Regnacq, C. y Schlick, J. (2022). Climate change, comparative advantage and the water capability to produce agricultural goods. World Development, 158, 105963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2022.105963
Cantillo, I. (2017). Perfil de competencias profesionales en negocios internacionales demandado por el sector productivo y las instituciones de educación superior en Santa Marta (Colombia). Negonotas Docentes, (9), 77-98. https://doi.org/10.52143/2346-1357.418
de Almeida, J., Ladeira, M., Faria, A. y Barbosa, M. (2021). A reference model for science and technology parks strategic performance management: An emerging economy perspective. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 59, 101612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jengtecman.2021.101612
de Andrés-Sánchez, J., Musiello-Neto, F., Rua, O. y Arias-Oliva, M. (2022). Configurational Analysis of Inbound and Outbound Innovation Impact on Competitive Advantage in the SMEs of the Portuguese Hospitality Sector. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(4), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc8040205
Delfín, F. y Acosta, M. (2016). Importancia y análisis del desarrollo empresarial. Revista Científica Pensamiento y Gestión, (40), 184-202. https://doi.org/10.14482/pege.40.8810
Donnelly, F., Gordon, S., Lawn, S., Schoo, A., Thomas, J. y White, K. (2023). Guarded reciprocity: A study of managers expectations of graduates interprofessional practice (IPP) skills and knowledge. Journal of Interprofessional Education & Practice, 31, 100620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xjep.2023.100620
Elia, G., Raguseo, E., Solazzo, G. y Pigni, F. (2022). Strategic business value from big data analytics: An empirical analysis of the mediating effects of value creation mechanisms. Information & Management, 59(8), 103701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2022.103701
Fan, S., Liu, G., Tu, Y., Zhu, J., Zhang, P. y Tian, Z. (2023). Improved multi-criteria decision making method integrating machine learning for patent competitive potential Evaluation: A case study in water pollution abatement technology. Journal of Cleaner Production, 403, 136896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136896
Ferrando, A. y Callohuanca, J. (2020). Incidencia de la capacitación en el desarrollo de habilidades gerenciales en los gerentes de pequeñas empresas del parque industrial de Villa el Salvador, Lima-Perú. Anales Científicos, 81(1), 1- 12. https://doi.org/10.21704/ac.v81i1.1494
García, F., Boom, E. y Molina, S. (2017). Habilidades del gerente en organizaciones del sector palmicultor en el departamento del Cesar - Colombia. Revista Científica Visión de Futuro, 21(2), 1-21. https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=357955446001
García, J., Duran, S., Cardeño, E., Prieto, R., García, E. y Paz, A. (2017). Proceso de planificación estratégica: Etapas ejecutadas en pequeñas y medianas empresas para optimizar la competitividad. Revista Espacios, 38(52), 16-30. https://acortar.link/n5oBGr
García, J., Paz, A. y Cantillo, N. (2019). Estrategia y habilidades para la competitividad: caso de pymes del sector construcción en Barranquilla. Aglala, 10(1), 312-339. https://doi.org/10.22519/22157360.1349
Gao, Q., Zhang, S., Cai, Z., Liu, K., Hui, N. y Tong, M. (2022). Understanding student teachers’ collaborative problem solving competency: Insights from process data and multidimensional item response theory. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 45, 101097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2022.101097
González, M. y Ley, J. (2019). Habilidades gerenciales y su influencia en la competitividad de las agroempresas del valle de Mexicali, México. Revista Espacios, 40(42), 16. https://www.revistaespacios.com/a19v40n42/a19v40n42p16.pdf
Gunawan, J., Aungsuroch, Y., Fisher, M., Marzilli, C., Nazliansyah, & Hastuti, E. (2023). Refining core competencies of first-line nurse managers in the hospital context: A qualitative study. International Journal of Nursing Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.08.001
Handayani, S. y Er, M. (2019). Antecedent and Business Process Management Non-Technical Capabilities in Social Media Implementation for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises: A Conceptual Model. Procedia Computer Science, 161, 1114-1121. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.11.223
Heubeck, T. (2023). Managerial capabilities as facilitators of digital transformation? Dynamic managerial capabilities as antecedents to digital business model transformation and firm performance. Digital Business, 3(1), 100053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.digbus.2023.100053
Hu, X. (2023). Application of a quality management model in the clinical laboratory for reporting of the critical values. Asian Journal of Surgery, 46(9), 4070-4071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2023.04.055
Ibarra, M., González, L. y Demuner, M. (2017). Competitividad empresarial de las pequeñas y medianas empresas manufactureras de Baja California. Estudios Fronterizos, 18(35), 107-130. https://doi.org/10.21670/ref.2017.35.a06
Kang, Y., Kim, R., & Whang, U. (2023). International knowledge transfers and capital structure of multinational affiliates: Evidence from expatriate managers as the transfer agents. Journal of Multinational Financial Management, 68, 100801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mulfin.2023.100801
Katz, R. (1974). Habilidades para una administración efectiva. USA: Editorial Biblioteca Harvard.
Lee, J. y Aghamohammadi, N. (2023). Restaurant managers knowledge and intention to improve building ventilation and indoor air quality using control measures in a middle-income country. Building and Environment, 244, 110775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110775
Lee, S., Lee, S. y Ryu, J. (2021). Do Competent Managers Hoard Bad News? Self-regulation Theory and Korean Evidence. Finance Research Letters, 41, 101836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2020.101836
Leyva, A., Espejel, J. y Cavazos, J. (2017). Habilidades gerenciales como estrategia de competitividad empresarial en las pequeñas y medianas empresas (Pymes). Perspectiva Empresarial, 4(1), 7-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.16967/rpe.v4n1a1
Magdaniel, Y., Sánchez, J. y Ucros, M. (2016). Competencias y éxito gerencial en empresas de servicios públicos, municipios de Riohacha y Maicao, Guajira, Colombia. Sotavento M.B.A., (27), 132-141. https://doi.org/10.18601/01233734.n27.10
Martínez, J., Cardeño, E., Ramírez, W. y Durán, S. (2017). Liderazgo transformacional como estrategia de adaptación en la gestión logística empresarial. Desarrollo Gerencial, 9(2), 140-157. https://doi.org/10.17081/dege.9.2.2980
Martínez, R., Hergueta, A. y Ayllón, M. (2020). ¿Hay suficiente número de plazas hospitalarias para las prácticas de nuestros alumnos de Formación Profesional? Revista Española de Patología, 53(4), 232-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patol.2020.02.007
Montoya, C. y Boyero, M. (2016). El recurso humano como elemento fundamental para la gestión de calidad y la competitividad organizacional. Revista Científica Visión de Futuro, 20(2), 1-20. https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=357947335001
Munastiwi, E. (2015). The Management Model of Vocational Education Quality Assurance Using ‘Holistic Skills Education (Holsked)’. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 204, 218-230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.08.144
Naranjo, R. (2015). Habilidades gerenciales en los líderes de las medianas empresas de Colombia. Pensamiento & Gestión, (38), 119-146. http://dx.doi.org/10.14482/pege.37.7020
Oppong, N. y Segbenya, M. (2023). Inter-sector managerial skills requirements in Ghana: Group interactive brainstorming approach. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 8(1), 100594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssaho.2023.100594
Pedraza, J., Ruiz-Vélez, A., Sánchez-Rodríguez, M. y Fernández-Esquinas, M. (2023). Management skills and organizational culture as sources of innovation for firms in peripheral regions. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 191, 122518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122518
Qian, C., Yu, K., Chen, N., Shen, W., Hou, S. y Lei, Y. (2023). When to adopt a new process management standard? An organizational learning perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 263, 108939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2023.108939
Sambasivan, M., Abdul, M. y Yusop, Y. (2009). Impact of personal qualities and management skills of entrepreneurs on venture performance in Malaysia: Opportunity recognition skills as a mediating factor. Technovation, 29(11), 798-805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2009.04.002
Sánchez, C. (2016). Planificación financiera de empresas agropecuarias. Revista Científica Visión de Futuro, 20(1), 209-227. https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=357943291006
Sarwar, H., Aftab, J., Ishaq, M. y Atif, M. (2023). Achieving business competitiveness through corporate social responsibility and dynamic capabilities: An empirical evidence from emerging economy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 386, 135820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135820
Schöck, M., Batora, M., Müller, J., Bursac, N. y Albers, A. (2023). Influence of Agility on the Innovation Capability of Organizations – A Systematic Review of Influencing Factors. Procedia CIRP, 119, 427-437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2023.03.105
Sehnem, S., Piekas, A., Dal, C., Fabris, J. y Leite, A. (2020). Public policies, management strategies, and the sustainable and competitive management model in handicrafts. Journal of Cleaner Production, 266, 121695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121695
Su, F., Mao, J. y Jarvenpaa, S. (2023). Organizational path transformation in response to disruptive environmental changes: The role of middle managers. Long Range Planning, 56(2), 102292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2022.102292
Suh, E., West, J. y Shin, J. (2012). Important competency requirements for managers in the hospitality industry. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 11(2), 101-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhlste.2012.02.005
Sun, C., Shute, V., Stewart, A., Yonehiro, J., Duran, N. y D'Mello, S. (2020). Towards a generalized competency model of collaborative problem solving. Computers & Education, 143, 103672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103672
Suriaga, M. y Gamboa, J. (2019). Habilidades Gerenciales de la Actualidad. E-IDEA Journal of Business Sciences, 1(1), 1-16. https://revista.estudioidea.org/ojs/index.php/eidea/article/view/5/2
Wang, J. y Cao, H. (2022). Improving competitive strategic decisions of Chinese coal companies toward green transformation: A hybrid multi-criteria decision-making model. Resources Policy, 75, 102483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102483
Wang, N., Wu, M. y Yuen, K. (2023). Assessment of port resilience using Bayesian network: A study of strategies to enhance readiness and response capacities. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 237, 109394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2023.109394
Whetten, D. y Cameron, K. (2011). Desarrollo de habilidades directivas (8va ed.) https://clea.edu.mx/biblioteca/files/original/f12eda1de07b7c59560816f683210111.pdf
FINANCING
No external financing.
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS (ORIGINAL SPANISH VERSION)
Se agradece a la Corporación Unificada Nacional de Educación Superior – CUN.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Diana Esther Álvarez Contreras, José David Montes Padilla and Cristian David Osorio Martínez.
Research: Diana Esther Álvarez Contreras, José David Montes Padilla and Cristian David Osorio Martínez.
Methodology: Diana Esther Álvarez Contreras, José David Montes Padilla and Cristian David Osorio Martínez.
Writing - original draft: Diana Esther Álvarez Contreras, José David Montes Padilla and Cristian David Osorio Martínez.
Writing - revision and editing: Diana Esther Álvarez Contreras, José David Montes Padilla and Cristian David Osorio Martínez.